What mushrooms grow in the fields in autumn. Autumn mushrooms and the risks of “silent hunting”
Autumn has arrived, and the popularity of “silent hunting” continues to actively gain momentum. At the same time, the number of its victims is increasing. Mushroom poisoning is not uncommon from spring to autumn, and even in winter they happen when homemade twists are used. But the more active the mushroom season, the more people seek emergency medical help with symptoms of poisoning. We figured out why mushrooms are dangerous for human health and life and why the number of victims does not decrease from year to year.
Going to the forest to pick mushrooms is a good tradition for many Russians. In the fall, you can see whole crowds of people who want to join in the “quiet hunt”, who head out of town together, tirelessly telling each other where the most mushroom places are. Boletuses, saffron milk caps, aspen boletuses, boletus mushrooms, moss mushrooms, milk mushrooms, white trumpets and, of course, honey mushrooms - this is not the entire list of what makes people look closely at their feet while walking through the forest. Moreover, not only avid mushroom pickers, but also those who know little about this topic take part in such a marathon.
Mushrooms are difficult to digest foods that only a relatively healthy person can handle. Both poisonous and conditionally edible gifts of nature contain toxins in varying concentrations, most often affecting the cells of the intestines, kidneys and liver. Even mushrooms that are considered edible, such as porcini or boletus, can pose a danger to the body if they are collected and prepared incorrectly. In order not to cause harm to health from conditionally and simply edible mushrooms, the following rules must be observed:
- take the right approach to choosing a collection site, choosing sites in environmentally friendly areas, away from roads and populated areas;
- collect only those mushrooms that you are confident in; if you have the slightest doubt about a particular specimen, immediately throw it away;
- cut only dense, worm-eaten mushrooms with whole stems;
- use wicker baskets for collection;
- Having brought your “prey” home, inspect it several times and sort it by type;
- cook mushrooms immediately after picking, without delaying until the next day.
It is worth noting that, no matter how you cook mushrooms, you must first boil them in salted water and then drain them.
Different mushrooms are perceived differently by the body of each individual person. For example, mushrooms called pigs are popular in the fall. Most often they are prepared for the winter and cooked by frying. To digest them, the human body must produce the enzyme glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase in sufficient quantities. Otherwise, eating pigs will lead to the development of gastroenteritis - inflammation of the mucous membrane of the stomach and small intestine.
Going into the forest without any experience, it is very easy to pick up a whole basket of inedible and poisonous mushrooms. Poisoning most often affects entire families or groups of friends who together consumed dishes from the forest “catch”. In most cases, victims are confident that they only collected edible mushrooms and adhered to all the rules for preparing them. But not everything is so simple, because the following “surprises” await us in the autumn forest.
Enemy #1. Pale grebe
This mushroom is often mistaken for various types lamellar edible mushrooms, mainly for russula, some varieties of champignons, honey mushrooms and rows. You can recognize it by its grayish-green cap and white stem with a thickening at the bottom. The pale grebe is very poisonous. Even just holding it in your hands and then rubbing your eyes or lips with these hands can cause significant harm to your health. If such a mushroom ends up with the others collected earlier, you will have to say goodbye to all the “prey”. What can we say if the poor toadstool ends up on the table! The poison contained in it is not destroyed by heat treatment, so poisoning is inevitable.
Toadstool contains amanitins. Lethal dose of such a toxin - 0.1 mg/kg of human body weight. 100 g of mushrooms contain approximately 10-15 mg of amanitins, therefore, just one toadstool can poison several people at once. It is worth noting that these toxins are water-soluble, so even a piece poisonous toadstool can turn a mass of edible mushrooms into an extremely dangerous treat. The first signs of poisoning by amanital mushrooms, which include pale grebe, appear after 6-16, or even more hours. First, victims begin to experience sharp abdominal pain, then they develop repeated vomiting and frequent loose stools, often mixed with blood. When the first symptoms of poisoning appear, you must urgently call " ambulance».
Enemy No. 2. Fly agaric and Patouillard fiber
Fly agarics and Patouillard fiber contain muscarine, an alkaloid that has a strong effect on the nerve centers. If fly agaric is easily identified externally, then Patuillary fiber, which is more poisonous and deadly, is often confused with russula. The first symptoms of ingestion of such a mushroom appear approximately half an hour after its consumption:
- At first, the patient experiences minor visual disturbances and profuse salivation;
- then vomiting and diarrhea appear, and blood pressure levels rise.
Death occurs in approximately 8-9 hours in the absence of timely medical care.
False mushrooms are the most common danger faced even by experienced mushroom pickers. False honey mushrooms, boletus, chanterelles and many other varieties of forest gifts most often end up on the dinner table. Symptoms of poisoning in this case appear 0.5-3 hours after eating. You must immediately call an ambulance, and drink plenty of water until the doctors arrive. room temperature, induce vomiting and take activated charcoal.
Among the so-called twin mushrooms you may accidentally end up in your basket in the fall:
- A gall mushroom that has an external resemblance to the most desirable prey of the “silent hunt” - the porcini mushroom. This lookalike is not edible because its flesh tastes very bitter.
- Pepper mushroom with very hot and hot-tasting flesh. It is easy to confuse it with boletus, goats or green moss.
- The gray-pink milkweed is a counterpart to the bitter mushroom, an edible mushroom that is usually salted or pickled, after being soaked to remove the bitterness. This mushroom is poisonous.
- False fox- a double of an ordinary fox, with maximum similarity to it. Refers to inedible mushrooms due to its hard flesh and lack of any nutritional value.
Separately, it is worth noting autumn honey mushrooms, which are most common in forests around mid-September. Honey mushrooms are distinguished by good taste qualities. They are used to cook soups, prepare sauces and gravies, salt, pickle and even dry. Autumn honey mushrooms usually grow in groups, so they are easy to collect. Besides autumn honey fungus Others may also be a good catch for an experienced mushroom picker. edible lookalikes, for example, meadow or winter honey fungus, golden or common scale.
The life-threatening counterparts of the autumn honey fungus are the sulfur-yellow and brick-red false honey fungus. Most often they can be found in deciduous forests. False honey mushrooms can be identified by the yellow or greenish-yellow, as well as the olive color of the plates. The brick-red false honey fungus has a brightly colored skin on its cap. As they mature, the plates of the sulfur-yellow false foam acquire a green tint; those of the brick-red one become brownish-green or black-brown. Also these dangerous doubles most often there is no characteristic ring on the leg, like a real autumn honey mushroom.
If you find a very large and visually attractive mushroom, do not rush to cut it off. After all, overripe mushrooms cannot be eaten. Even if worms have not yet colonized it, mushrooms that are too large in size and soft to the touch are already spoiled. The longer the mushroom grows, the more breakdown products of fatty substances and proteins are formed in it. The same applies to mushrooms, the processing and preparation of which after cutting is delayed even for a day. Toxins produced in old mushrooms affect nervous system, disrupt the heart rhythm, and also lead to disorders of the respiratory and digestive systems.
Enemy #5. Mushrooms are like sponges
Even edible mushrooms, if they grow in contaminated areas, can lead to poisoning. They are like a sponge, absorbing all substances from the environment. Thus, nitrates, pesticides, heavy metals, etc. can accumulate in mushrooms. You cannot collect them along roads, in close proximity to industrial enterprises and in places where garbage accumulates. No matter how attractive, for example, whole groups of black milk mushrooms growing nearby, which can be found along roads, may seem, they cannot be collected. It is also not recommended to collect mushrooms under power lines.
The most susceptible to the environment and instantly absorbing all harmful elements are porcini mushrooms and champignons.
First of all, it is not recommended to eat mushrooms for children under 14 years of age, pregnant and lactating women, as well as the elderly. This product is also contraindicated for those who have chronic diseases organs gastrointestinal tract. Even relatively healthy people It is advisable to eat mushrooms in limited quantities to avoid excessive stress on the gastrointestinal tract.
It is worth noting that although mushrooms are low-calorie product(350-380 kcal per 1 kg), it does not belong to the dietary category. This is due to difficult-to-digest protein, which requires special effort from the body and a lot of time.
The most necessary things for every mushroom picker are a mushroom picker's calendar and a mushroom guide. By checking the mushroom calendar, you can easily understand which mushrooms to pick at this particular time. Despite the fact that the timing of the appearance of a particular type of mushroom is not constant and depends on weather conditions, each mushroom has its own specific dates for the beginning and end of the season. These are what the mushroom picker’s calendar for 2017 contains. If you have forgotten the main differences between poisonous mushrooms and edible ones, be sure to refresh your memory by looking at the mushroom guide.
Mushroom picker calendar for summer
- Mushrooms in June. According to the mushroom picker's calendar, in the first ten days of June, those who like to pick mushrooms should look for boletus in the pine forest, and boletus mushrooms in the birch groves. In the second half of June comes mushroom season at the white loaders. Pogruzdki are fruitful mushrooms; they are collected all summer and until late autumn.
- Mushrooms in July. In early July, the season of saffron milk caps begins, and at the end of the first ten days of July, the most desirable for mushroom pickers are porcini mushrooms. At the same time, according to the calendar, the first russula appear - the most productive mushrooms. They can be found in almost any forest from July until late autumn frosts. In the second half of July, milk mushrooms and black milk mushrooms begin to be found in coniferous and mixed forests, and on the edges and forest clearings Mushroom pickers are delighted with chanterelles and pigs.
- Mushrooms in August. August is considered the most mushroom month. In fruitful years, mushroom pickers in August collect porcini mushrooms, milk mushrooms, saffron milk caps, boletus mushrooms, porcini mushrooms, russula, boletus and other mushrooms in baskets. At the beginning of August, the first honey mushrooms appear, and in the middle of the month - moths and white mushrooms. Second half of August and first ten days of September - best time for collecting mushrooms.
Mushroom picker calendar for autumn
- Gibs in September. Mushroom pickers are happy in September. As the mushroom picker's calendar says: many summer mushrooms continue to grow, while at the same time autumn mushrooms appear in large quantities. In the second half of September, some species of mushrooms disappear, but honey mushrooms, volushki, white caps, boletus mushrooms, pigworts, and white cape mushrooms are still abundant.
- Mushrooms in October. At the end of October, you can postpone the mushroom picker's calendar until next year, because the mushroom season is ending. In the second ten days of October, when the average daily air temperature drops to 4-5 degrees Celsius and night frosts begin, the mushroom picking season will end. However, you can still find young honey mushrooms preserved under the foliage and grass of saffron milk caps, saffron milk caps and white mushrooms.
Mushroom picker calendar for 2017
The mushroom picker's phenological calendar will come to the aid of beginning mushroom pickers. The mushroom picker's calendar marks the most popular mushrooms and the period when to collect these mushrooms in the forest. Of course, everything depends on the region and the weather in each season, but some useful knowledge When to pick mushrooms, the mushroom picker's calendar gives you the full answer. You will also find it useful
| What mushrooms to collect |
When to pick mushrooms |
||||||
| April | May | June | July | August | September | October | |
| Morels | + | + | + | - | - | - | - |
| Stitches | + | + | + | - | - | - | - |
| May mushroom | - | + | + | - | - | - | - |
| Oyster mushroom | - | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| Meadow honey fungus | - | - | + | + | + | + | - |
| boletus | - | - | + | + | + | + | - |
| Oiler grainy | - | - | - | + | + | + | - |
| Summer honey fungus | - | - | + | + | + | + | + |
| The fox is real | - | - | - | + | + | + | - |
| White mushroom | - | - | + | + | + | + | + |
| Boletus | - | - | + | + | + | + | + |
| Pluteus deer | - | - | + | + | + | + | + |
| Spiky raincoat | - | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| Common champignon | - | - | + | + | + | + | - |
| Field champignon | - | - | - | - | + | + | - |
| Valuy | - | - | - | + | + | + | - |
| Funnel talker | - | - | - | + | + | + | - |
| White umbrella mushroom | - | - | - | + | + | + | - |
| Variegated umbrella mushroom | - | - | - | + | + | + | + |
| Real milk mushroom | - | - | - | - | + | + | - |
| Poddubovik | - | - | - | + | + | + | - |
| Ivyshen | - | - | - | - | + | + | + |
| Loader white | - | - | - | - | + | + | - |
| Loader black | - | - | - | - | + | + | - |
| Fat pig | - | - | - | - | + | + | - |
| Russula yellow, food, etc. |
- | + | + | + | + | + | - |
| Green moss | - | - | + | + | + | + | + |
| Yellow hedgehog | - | - | - | - | + | + | - |
| Ringed cap | - | - | - | + | + | + | - |
| Larch oiler | - | - | - | + | + | + | - |
| Volnushka pink | - | - | - | - | + | + | + |
| Black breast | - | - | - | + | + | + | + |
| Spruce green camelina | - | - | - | - | + | + | + |
| Pine mushroom | - | - | - | - | + | + | + |
| Gray talker | - | - | - | - | + | + | - |
| Late oiler | - | - | - | - | + | + | - |
| Winter mushroom | - | - | - | - | - | + | + |
| Loader black and white | - | - | - | - | - | + | + |
| Polish mushroom | - | - | - | - | + | - | - |
| Autumn oyster mushroom | - | - | - | - | - | + | - |
| Gray row | - | - | - | - | - | + | - |
| Autumn stitch | - | - | - | - | - | + | + |
| Autumn honey fungus | - | - | - | - | - | + | + |
| Row purple | - | - | - | - | + | + | - |
| Greenfinch | - | - | - | - | + | + | + |
| Hygrophor brown | - | - | - | - | - | + | + |

Mushroom picker calendar 2017
for the Moscow region and central Russia
| Types of mushrooms | May | June | July | August | September | October | ||||||||||||
| Decades | ||||||||||||||||||
| I | II | III | I | II | III | I | II | III | I | II | III | I | II | III | I | II | III | |
| Morel | ||||||||||||||||||
| White mushroom | ||||||||||||||||||
| Boletus | ||||||||||||||||||
| boletus | ||||||||||||||||||
| Chanterelle | ||||||||||||||||||
| Oiler | ||||||||||||||||||
| Mosswort | ||||||||||||||||||
| Honey fungus | ||||||||||||||||||
| Ryzhik | ||||||||||||||||||
| Volnushka | ||||||||||||||||||
| Gruzd | ||||||||||||||||||
| Valuy | ||||||||||||||||||
| Russula | ||||||||||||||||||
| Champignon | ||||||||||||||||||
| Belyanka (white volnushka) | ||||||||||||||||||
| Gorkushka | ||||||||||||||||||
| Greenfinch | ||||||||||||||||||
| Serushka | ||||||||||||||||||
| Kozlyak | ||||||||||||||||||
| Raincoat | ||||||||||||||||||
| Cap | ||||||||||||||||||
| Ryadovka | ||||||||||||||||||
| Violin | ||||||||||||||||||
Mushroom picker calendar 2017
for the Leningrad region and northern places of Russia
The mushroom season in the forests of the Leningrad region is from August to November. Mushroom places There are countless varieties in the Leningrad region, the main thing is to know when to pick this or that mushroom. The mushroom picker calendar for the Leningrad region will help with this. Edible mushrooms in the Leningrad region are diverse: these include bright aspen mushrooms and delicious boletus mushrooms, valuable porcini and boletus mushrooms, red chanterelles, slippery boletus and moss mushrooms, as well as red mushrooms, milk mushrooms and honey mushrooms. If you check the mushroom picker's calendar, you can pick up delicious morels, puffballs, and russula. Don’t be lazy, if the weather is right after the rain, look at the mushroom calendar and get ready for a mushroom trip. Refer to the mushroom picker calendar below for the Leningrad region.
| Mushroom picker calendar for the Leningrad region | ||
| When to pick mushrooms | What mushrooms to collect | Where to pick mushrooms |
| March | Oyster mushroom, tree mushrooms, talker | There are practically no mushrooms, but at the end of the month the first snowdrops may appear. If the winter is warm, you can find fresh oyster mushrooms. Oyster mushrooms usually grow on trees, the cap of such a mushroom is one-sided or rounded, the plates run down to the stem, as if growing to it. It is not difficult to distinguish oyster mushrooms from inedible mushrooms - it has a cap that is completely leathery to the touch. |
| April | Oyster mushroom, tree mushrooms, govorushka, morel, stitch | Snowdrop mushrooms are quite common - morels and stitches |
| May | Morel, stitch, oil can, oyster mushroom, raincoat | Most mushrooms can be found not under trees, but in clearings, in thick grass. |
| June | Butterfly, boletus, boletus, oyster mushroom, morel, honey fungus, chanterelle, porcini mushroom, raincoat | In June, mushrooms of the highest (first) category begin to appear. |
| July | Oiler, boletus, boletus, oyster mushroom, morel, puffball, honey fungus, chanterelle, porcini mushroom, moss mushroom | There are already quite a lot of mushrooms - both in the clearings and under the trees. In addition to mushrooms, strawberries and blueberries are already found. |
| August | Oiler, boletus, boletus, oyster mushroom, morel, honey fungus, chanterelle, porcini mushroom, moss mushroom | At this time, mushrooms can be found almost everywhere: in the grass, under trees, near stumps, in ditches and on trees, and even in city squares and on the sides of roads. In addition to mushrooms, lingonberries have already ripened, and cranberries are appearing in the swamps. |
| September | Oiler, boletus, boletus, oyster mushroom, morel, honey mushroom, chanterelle, porcini mushroom, moss mushroom, | September is the most productive month for mushrooms. But you need to be careful: autumn is coming to the forests, and in the bright foliage it is difficult to see the multi-colored mushroom caps. |
| October | Valuy, oyster mushroom, camelina, honey fungus, champignon, boletus, porcini mushroom, milk mushroom, moss mushroom, russula | The number of mushrooms in the clearings begins to decrease. In October, it is better to look for mushrooms near stumps and under trees. |
| November | Butterfly, greenfinch, oyster mushroom, tree mushrooms. | Frosts are beginning, but there is a high probability of finding frozen mushrooms. |
You will also find useful material about mushrooms with a mushroom picker’s calendar:
Mushroom key
There are no reliable methods for distinguishing edible and poisonous mushrooms by eye, so the only way out is to know each of the mushrooms. If the species identity of mushrooms is in doubt, you should under no circumstances eat them. Fortunately, among the hundreds of species found in nature, many have such clearly defined characteristics that it is difficult to confuse them with others. However, it is better to always have a mushroom identification guide on hand.
Mushroom Guide - How to distinguish edible mushrooms |
|
 |
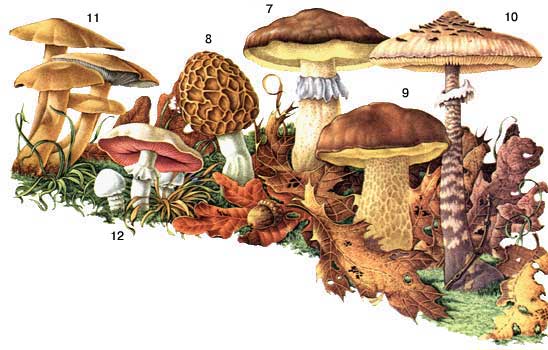 |
| 1 - breast; 2 - saffron milk cap; 3 - cone mushroom; 4 - greenish russula; 5 - edible russula; 6 - fox. |
7 - oiler; 8 - morel; 9 - porcini mushroom; 10 - large umbrella; 11 - row; 12 - field champignon. |
Mushroom identification guide - How to distinguish poisonous mushrooms |
|
 |
 |
| 1 - paneolus; 2 - gray float; 3 - glowing talker; 4 - common veselka; 5 - pale grebe; 6 - white fly agaric (spring). |
7 - red fly agaric; 8 - variegated champignon; 9 - russula emetic; 10 - value; 11 - entoloma |
Taking a mushroom guide and a mushroom picker's calendar with you as you make your way through the forest in search of mushrooms, you can entertain yourself with a conversation about mushrooms. Share with friends interesting facts about mushrooms.
The most poisonous mushrooms
There are about a hundred definitely poisonous species of mushrooms in Europe. Of these, only eight are deadly poisonous.
- The most poisonous mushroom is Galerina sulciceps, which grows in Java and Sri Lanka. Even one eaten fruit leads to death in half an hour or an hour.
- In Europe and in North America The most poisonous are the white (spring) fly agaric and the stinking fly agaric.
- The most poisonous and deadly to humans is the toadstool, for which no antidote has yet been found.
The largest edible mushrooms
The largest mushroom in the world grows in Malheur National Park in the Blue Mountains (Oregon, USA). This mushroom covers an area of 890 hectares. However, we are interested in edible mushrooms.
- The biggest edible mushroom was discovered in Canada by Jean Guy Richard. The unique raincoat (Calvatia gigantean) had a circumference of 2.64 meters and a weight of 22 kilograms.
- The largest champigno was found in Italy by Francesco Quito in the province of Bari. The mushroom weighed 14 kilograms.
- The largest truffle found weighed even less - only 7 kilograms.
The most expensive mushrooms
- Of course, the most expensive mushrooms are truffles, white and black. Incredibly expensive white truffles grow mainly in Italy, in the Piedmont region. The Perigord black truffle or Tuber melanosporum is also considered a real masterpiece of nature.
- The matsutake mushroom competes with truffles for the title of the most expensive mushroom. This mushroom is often called the king of mushrooms due to its rich mushroom aroma and excellent taste. No one has yet managed to grow matsutake artificially, which is why the price for them has increased significantly, unlike truffles, which the Chinese have learned to successfully cultivate.
Now, thanks to the mushroom picker's calendar, you know what mushrooms to pick and when to pick them in the Moscow and Leningrad regions. A short mushroom guide will help you distinguish edible and poisonous mushrooms. Happy quiet hunting.
Autumn has come, which means you can already go in search of porcini mushrooms, birch mushrooms, aspen mushrooms, milk mushrooms, saffron milk caps, butter mushrooms and others, no less delicious mushrooms! How interesting it is to look for real finds among the fallen autumn leaves, because everything collected with your own hands becomes the most valuable!
What mushrooms can be found in the autumn forest?
1. White mushroom
The old boletus, as it is popularly called, is not white at all, but very brown, with a yellowish leg. So why is it called white? It's as simple as that - if you break it in half, you can see the snow-white pulp, which will not change color even if it is dried. The porcini mushroom is the king of mushrooms, it is very nutritious and is considered a delicacy. It can be prepared for every taste: stewed, fried, made into soups and sauces, and even eaten raw! Porcini mushrooms contain substances that prevent the occurrence of tumors and improve heart function.

2. Berezovik
It is also called boletus, of course - it’s immediately clear where to look for it! It grows in deciduous and mixed forests. The flesh of the birch tree is white and does not change color when cut. The hat can be white, yellow, brown, sometimes even black. It can be eaten fried, pickled, salted or dried.

3. Aspen
Boletus is a mushroom of good luck. It is really very difficult to find; experienced mushroom pickers may not encounter it for a long time, and a beginner will find it in a matter of minutes! It grows in mixed forests. These mushrooms can be found before the beginning of winter, namely the first frost. His hat is red-orange, but despite his eye-catching coloring, he is very, very difficult to find. Prepared from boletus delicious soups and salads, they are boiled, fried and pickled.

4. Milk mushrooms
Milk mushrooms do not like loneliness; they grow in families and heaps. The mushrooms are dense and heavy in structure, their cap is white, slightly yellowish. These mushrooms grow in deciduous and mixed forests. Milk mushrooms were considered the most delicious mushrooms Ancient Rus', while in the West they were considered completely inedible. Currently, milk mushrooms are soaked and then salted.
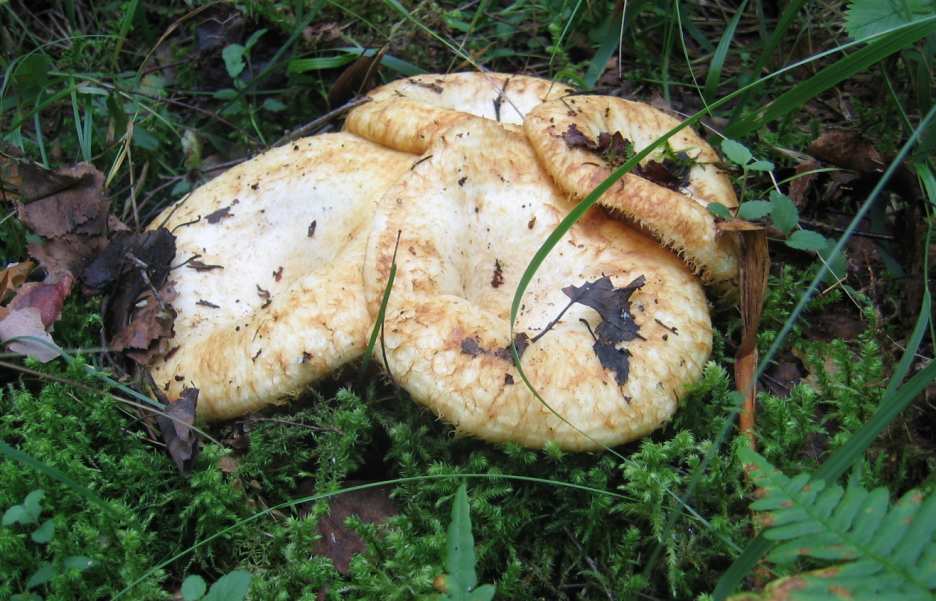

5. Ryzhik
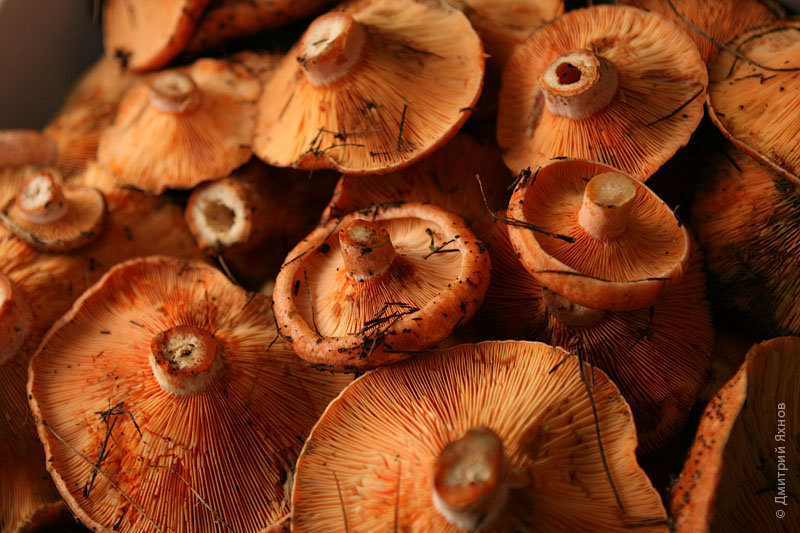
Red, red, freckled... Ginger is a beautiful and elegant mushroom that even kings did not disdain to eat. These mushrooms are red on all sides, even their juice is orange. That's why they got their name. If the porcini mushroom is the king, then the saffron milk cap will get the title of the great mushroom prince. It can be prepared in any form, except that it is not advisable to dry it. Salted and pickled mushroom is considered a real delicacy. Saffron milk caps are simply a storehouse of vitamins, they have a lot of useful properties, improve metabolism and suppress the development of bacteria.

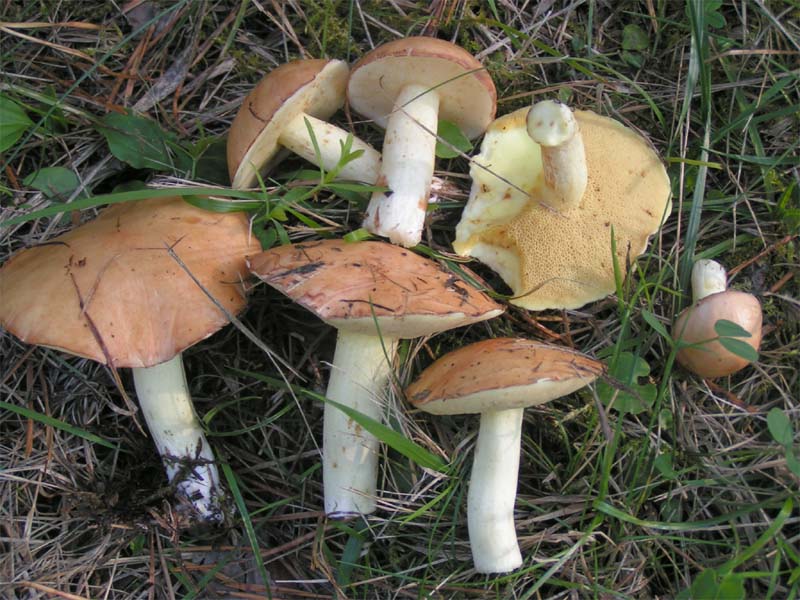
6. Butter
Collecting boletus is real fun! They grow in large groups, families, just fill the basket! They are cut off immediately under the cap. These mushrooms are suitable for any type of cooking, but it is better to remove the mucous skin from the cap.

As we can see, there are plenty of mushrooms in the fall! Choose - I don’t want to. But it should be remembered that poisonous mushrooms are surprisingly similar to their noble relatives. The consequences of mushroom poisoning are very significant, because one poisonous mushroom can poison the entire pan! How to test mushrooms for toxicity when cooking? You can find out on the portal. You will also be able to watch online all episodes of the program about the most important things, you will learn a lot useful information and expand your horizons.
Especially for fashion magazine about beauty, health, relationships and comfort at home






