Rat poison: lethal dose for humans, necessary assistance in case of poisoning. Therapy after poisoning with rat poison
Not all people who like to eat mushrooms are good mushroom pickers. As a result, many of them are unable to distinguish edible mushrooms from poisonous ones. This causes accidental eating edible species mushrooms.
Mushroom intoxication is the most complex food poisoning that can cause death.
What should be done to avoid such a dangerous consequence? How to provide first aid to a poisoned person?
Usually after eating good mushrooms, after 2-3 hours, the first symptoms of poisoning of the body begin to appear. The time depends on the type of mushrooms consumed, on the method of processing them, on the body weight of the affected person, on his age, on the dose of the toxin that has entered the body.
You need to know that some mushrooms may not make themselves felt immediately, the symptoms begin to appear 10-14 days after eating such widows. These are mushrooms such as lepiota and cobweb.
Signs of intoxication are similar to the symptoms that occur with food poisoning:
- Diarrhea occurs;
- The person begins to feel sick, severe vomiting occurs;
- There is severe pain in the abdomen.
However, there are some symptoms that differ from the general ones, they depend on the type of non-edible mushrooms consumed and on the amount eaten. Most often there are such poisonings:
- When poisoned with a pale toadstool, muscle pain occurs, which spreads throughout the body, vomiting, nausea, and severe diarrhea. In vomit, as well as in feces, blood impurities may be present. The chair is frequent (about 20-25 times a day). The vomit is like coffee grounds. A convulsive syndrome develops very quickly, the work of the cardiovascular system is disrupted, respiratory function is inhibited, kidney failure, jaundice develops, a person can fall into a coma.
- Mushrooms such as lines, morels, except common features, provoke the development of a convulsive syndrome. When poisoned with such mushrooms, the spleen increases significantly in size, the kidneys fail, the red blood cells in the bloodstream are destroyed, the liver suffers (it becomes large, jaundice joins). The person loses consciousness.
- When eating red fly agaric, the symptoms appear very quickly - in half an hour or an hour. In humans, the production of saliva increases, the formation of sweat increases, the pupil narrows, there is a convulsive syndrome, the arterial pressure, the heartbeat slows down, the patient's consciousness is disturbed.
- When eating a panther fly agaric, the pulse quickens, the pupil becomes dilated, the mucous membranes of the skin are dried, the same applies to the mucous membranes.
The child's body is much more sensitive to the effects of poisons, so they will show signs of mushroom poisoning much faster, and the condition itself will be more difficult.

Women in the position are especially difficult to tolerate mushroom poisoning, because toxins can pass through the placenta and affect the calf. There is a high risk of miscarriage. The patient begins to have a severe headache, she refuses to eat, there is diarrhea, vomiting, dizziness and nausea.
Loss of fluid, provoked by diarrhea and vomiting, can cause dehydration, loss of vitamins and minerals. In case of poisoning, the pulse may increase, blood pressure may decrease.
First aid
When the first symptoms of intoxication occur, an urgent need to call a medical team. The remains of mushrooms should not be thrown away, as they will be needed in the future for the study. This will greatly simplify the selection of the correct treatment, because it will be possible to identify the exact type of poison.
Before the arrival of doctors, it is important to begin providing first aid to the victim.
First aid for intoxication is as follows:
- Initially, you need to drink the victim, giving him to drink at least 1.5-2 liters of water. Then gently press on the root of the tongue to artificially induce vomiting. Such measures are performed to cleanse the stomach of the remnants of fungi. If we are talking about pregnant women, then this technique is contraindicated for them.
- If there is no diarrhea, then the victim is given castor oil to drink - 1 tbsp. l;
- In order for the removal of toxins from their body to be accelerated, it is important to give the patient any remedy from the group of sorbents to drink. Quite suitable. Before use, it is important to read the instructions in order to find out the correct dosage.
- A plentiful drinking regimen is also very important. It is necessary to solder a poisoned person with black strong tea, non-carbonated water.
Treatment
In case of intoxication, therapy should be carried out in a hospital - in the toxicology department. The following actions are performed:
- Specialists using a special probe.
- Salt-based laxatives are prescribed, a special solution is injected into the vein and forced diuresis is carried out.
- In the first 24 hours, hemosorption is done.
Means are also prescribed for the treatment of kidney failure and disorders of the cardiovascular system. If intoxication was provoked by the red fly agaric, a specific antidote is used. This is Atropine. dosage in each separate case individually selected by the doctor.
In case of poisoning with mushrooms, it is forbidden to drink alcohol, use painkillers, drugs against diarrhea and vomiting.
Prevention
In order not to get poisoned by mushrooms, you need to follow these simple but effective rules:
- When picking mushrooms, only those species in which you have no doubt should be placed in the basket. If there is even the slightest doubt about the edibility of a particular mushroom, then such an individual should be thrown away.
- It is forbidden to take worm mushrooms or very old.
- Before placing the mushroom in the basket, inspect it carefully - look at the color of the cap, the presence and color of the plates.
- Mushroom picking is prohibited in environmentally polluted places. The fungus can absorb all the poisons and toxins that are in the places of their growth.
- Collected mushrooms are recommended to be cooked immediately.
Consequences of poisoning
The consequences of mushroom intoxication are very dangerous, especially without therapy.
The main reason is not knowing the signs that distinguish poisonous mushrooms from edible ones. Mushroom toxins, affecting all organs and systems in the body, can cause death in 2-3 days.
mushroom poisoning
Many people know how severe mushroom poisoning is. A similar problem is often faced by children, persons without a fixed place of residence and people who are not versed in this matter. Mushrooms grow almost everywhere. They can be found both in the forest and in the garden or in the country. Most of them are inedible. Others must be properly processed before being eaten. Poisoning proceeds according to the type of food intoxication.
Poisoning by various types of fungi
Mushrooms is a separate kingdom of wildlife. Only those that do not contain toxic substances are eaten. Not every person is well versed in what can be collected and eaten, and what is better not to cut. This is especially true for residents of large cities. Rural citizens live closer to the forest and get sick less often.

Types of mushrooms
In Ukraine there is the city of Kherson. There are a lot of mushroom pickers there. You can get poisoned by raw, boiled, fried or canned foods. In the latter case, we are talking about botulism. There are the following types of mushrooms:
- poisonous;
- conditionally edible (partially safe);
- fit for food.
The first group includes various grebes (pale and spring), smelly fly agaric, umbrellas, cobwebs, some varieties of lepiot. Partially safe mushrooms are false mushrooms, pigs, blackies, lines. You need to recognize them in the process of collecting and buying. Edible fungi include porcini, chanterelles, mushrooms, milk mushrooms, russula, volnushki, boletus, boletus, boletus - this is not the whole list. Many of them are not recommended to be eaten raw.
The city of Kherson is famous for its variety of mushrooms. A large number of poisoning cases are caused by false fungi. They have some differences. The greatest danger to humans is the pale grebe. 1 mushroom can lead to severe intoxication and damage to vital organs. Often, getting a toadstool into the stomach ends in the death of a person. The opinion that death is possible with the use of one fly agaric is erroneous, since for this you need to eat about a bucket of these mushrooms.
Danger of the pale toadstool
Which mushrooms are the most dangerous, not everyone knows. Often such a diagnosis is made as food intoxication against the background of the use of pale toadstool. She can get into the dish by accident, or if the mushroom picker was inexperienced. After what time the symptoms appear, not everyone knows. The incubation period is from 6 to 36 hours.
Symptoms and signs are caused by the ingestion of amanitotoxins. They are not destroyed by heat treatment. The lethal dose is 1 mushroom. The first manifestation of poison entering the blood is a general malaise. This is manifested by headache, sweating, chills. In the absence of proper treatment, the consequences of poisoning are very serious.

How long does it take for symptoms to appear internal organs known to every experienced toxicologist. This is just as important as the prevention of mushroom poisoning. Signs of intoxication are found in the first 2-3 days. The following complaints may appear:
- pain in the abdomen, similar to colic;
- liquid and frequent stools with an admixture of blood (melena);
- indomitable vomiting;
- bleeding;
- nausea;
- excitement;
- hallucinations;
- thirst;
- jaundice;
- anuria.

After some time, a coma develops. Toxins can have a damaging effect on the liver, brain, and kidneys. Only an experienced attending physician can distinguish intoxication with a pale toadstool from another acute pathology. If help is not provided on the first or second day, then the mortality rate reaches 50%. This is due to the impact on the body of phalloin, amanitin and phalloidin.
Why fly agarics are dangerous
Almost every child and adult has seen fly agarics. They grow in any city, including Kherson. These are beautiful mushrooms with bright colors. The toxins they contain (muscarine, muscaridine) act on the nervous system. A person poisoned by fly agarics will not die, but serious consequences are possible. Poisoning poisonous mushrooms fly agaric is characterized by a faster occurrence of complaints. The term is from 20-30 minutes.
For several hours, intoxication of the body may not appear. The first signs of mushroom poisoning include disruption of the brain and digestive organs. When using red fly agaric, productive cough, shortness of breath, pupillary constriction, abdominal pain, decreased heart rate, and diarrhea are disturbing. Toadstool and porphyry fungus intoxication can manifest itself with hallucinations and euphoria. characteristic hypersalivation. Pickled fly agaric is also dangerous for humans. Mushroom poisoning manifests itself as clouding of consciousness. This is observed when eating panther fly agaric.
What are the dangers of pickled and salted mushrooms

Pickled and salted mushrooms
The prevalence of poisoning by poisonous mushrooms and plants is quite high. Their conservation is no less dangerous, poisonous mushrooms can accidentally get into the jar, or they are a factor in the transmission of the causative agent of botulism. This is a dangerous disease caused by the ingestion of a toxin into the human body. The latter is formed during the accumulation and reproduction of clostridia in a jar.
Botulism is a type of fungal food intoxication caused by the influence of bacterial waste products on the body. It can be a butter dish, white, redhead, champignon or mushroom. Not everyone knows how to avoid mushroom poisoning as a result of their salting and pickling. Toxins and bacteria accumulate in a vacuum, so it is dangerous to roll up jars of mushrooms.
Intoxication can occur after purchasing a product with a swollen cap or expired. Botulism is more common among young people. The following symptoms of mushroom poisoning are possible:
- nausea;
- vomit;
- diarrhea;
- dysphagia;
- dry skin;
- decreased vision;
- diplopia;
- pupil dilation;
- dyspnea.

Later speech becomes difficult. Possible increase in pressure. This pathology is life threatening. In case of poisoning with salted mushrooms, the development of intestinal paresis is possible.
The danger of edible mushrooms
You need to know the causes of mushroom poisoning, which are widely used in food. When collecting them, it is important to know certain rules. The causes of intoxication can be:
- the use of worm mushrooms in food;
- radiation pollution;
- gathering near major highways and within the city;
- improper storage;
- insufficient processing;
- application for salting dishes made of aluminum;
- intolerance this product.
Often, intoxication occurs with oils. This is possible if the fungi were overgrown and wormy. A poisoning agent is not always a toxin. There are a huge number of cases of intoxication with toxic compounds that have fallen on fungi from the external environment. These include salts of heavy metals and radioactive compounds. Signs of poisoning may appear when porcini mushrooms are combined with alcohol. Intoxication also occurs with improper cooking. Some mushrooms must be soaked, dried or boiled with a change of water before use.
What to do in case of poisoning

Treatment of mushroom poisoning should be carried out at the first symptoms. An urgent first aid plan is required. If poisoning is suspected canned mushrooms or fresh, then you need to do the following:
- induce a gag reflex;
- rinse the stomach thoroughly boiled water or saline;
- cleanse the intestines;
- take an antidote;
- see a doctor.
Regardless of the cause of mushroom poisoning, you need to call ambulance. Before her arrival, it is required to clean the gastrointestinal tract. To vomit, press on the root of the tongue or drink salted water. You can use special tools. First aid for mushroom poisoning does not end there.
Before washing the stomach, you need to drink a lot of boiled, warm liquid. It's better to use a probe. In case of mushroom poisoning, first aid includes an enema or the introduction of a saline laxative. If a pale toadstool was eaten, then Benzylpenicillin is prescribed. When using fly agaric, Atropine is indicated. Treatment for poisoning involves the use of activated carbon or other enterosorbent.

Drink with green tea and lemon
They do not allow the poison to be absorbed. The prognosis for life and health depends on how quickly first aid is provided for poisoning with poisonous mushrooms. With severe pain, NSAIDs or analgesics are prescribed. After the first medical aid has been provided for mushroom poisoning, a strict regimen must be observed. This is also required if the plant has become the cause of intoxication. Diet after poisoning is important aspect therapy.
The patient needs to drink more fluids. Suitable green tea lemon drink, fruit drink and infusion based on rose hips or raspberries. After providing first aid for mushroom poisoning, it is necessary to monitor vital signs (respiratory rate, heart rate, pressure). The doctor conducts a differential diagnosis.
For mushroom poisoning, treatment often includes infusion therapy. This allows you to reduce the symptoms of intoxication. In acute poisoning, complications are possible. After how long they come, not everyone knows. Mushroom poisoning can cause damage to the liver, kidneys and central nervous system.
Methods for the prevention of intoxication
You need to know not only how long mushroom poisoning occurs, but also how to prevent it. For this, the following rules must be observed:

- do not buy dried or canned foods at strangers;
- entrust picking mushrooms to a professional;
- exclude gathering near roads, mines, factories, factories and airports;
- do not touch pale toadstools;
- do not let children alone into the forest;
- qualitatively process conditionally edible mushrooms;
- refuse to use toadstools and fly agarics.
Kherson is a city in Ukraine where poisonings often occur. Not everyone knows how to prevent intoxication. With mushroom food poisoning, the symptoms are non-specific and very serious. It is not always possible to save the sick. To avoid negative consequences, precautions must be taken. Prevention of mushroom poisoning should be carried out in relation to people of all age categories, including children. Toadstool can be identified by white color. Fly agaric is often red. Majority inedible mushrooms have white juice. They are bitter in taste.
To exclude poisoning with porcini mushrooms, it is necessary to boil or fry them before use. It may happen that harmless boletus or champignons lead to organ damage. The reason for this is their improper storage. They must be refrigerated before use. Only young mushrooms with a dense stem and cap, which the city of Kherson is famous for, are useful.
All this is the primary form of prevention. If, for any reason, the poison has entered the body, then emergency care is required for mushroom poisoning. To prevent complications, you should immediately consult a doctor or call an ambulance. How to recognize mushroom poisoning is known to all experienced professionals. Thus, food intoxication is very common among the population. Poisonous mushrooms are no less dangerous to humans than plants and microbes.
All-Russian Olympiad for Schoolchildren in Biology
All-Russian Olympiad for Schoolchildren in Biology
All-Russian Olympiad for Schoolchildren in Biology
MUNICIPAL STAGE 2012/2013 G.
THEORETICAL TOUR
Grade 10
Part IYou are offered test tasks that require the choice of only one answer out of four possible. Maximum amount points that can be scored - 50 (1 point for each test task). The index of the answer that you consider the most complete and correct, indicate in the answer matrix.
The fundamental properties of living things are:
B) self-regulation and self-reproduction; +
C) integrity and discreteness;
D) ontogeny.
The first appearance of multicellular organisms is noted in:
B) the Paleozoic era;
B) Mesozoic era
D) the Cenozoic era.
A viral disease in humans is:
B) malaria;
B) encephalitis; +
D) pneumonia.
Bacteria have the ability to form spores.
B) rod-shaped; +
B) all forms;
D) a + b.
The peculiarity of radishes to complete individual development with the formation of seeds under long day conditions is called:
B) geotropism;
B) chemotropism;
D) photoperiodism. +
The object of biological research - penicillium, the image of which is shown in the figure, refers to:
| a) bacteria B) mushrooms; + D) animals. |
It is difficult to save a person who has been poisoned by deadly poisonous mushrooms, because:
B) mushrooms contain a lot of toxic substances;
C) mushroom poisons are very quickly dissolved and absorbed;
D) symptoms of poisoning appear after 12-24 hours, when the action of toxins is irreversible. +
The most important condition life of most green plants is:
B) the presence of ready-made organic substances necessary for their nutrition;
C) living in conditions of symbiosis with other organisms;
D) adequate lighting. +
The homeland of the cinnamon tree, from the bark of which the spice cinnamon is obtained, is:
B) southern Ethiopia;
B) South America
D) Sri Lanka (Ceylon); +
From the zygote of moss cuckoo flax is formed:
B) leafy plant;
C) small multicellular outgrowth;
D) a long thin thread - protonema.
In the temperate zone, it does not drop leaves for the winter:
B) blueberries;
B) cranberries; +
d) hawthorn.
The vertical flow of photosynthesis products in the stem of a woody plant is carried out according to:
B) bast fibers;
B) wood parenchyma;
D) core rays.
How many species are there in the Flowering department at present?
B) more than 500 thousand species;
C) more than 250 thousand species; +
D) about 100 thousand species.
The hostess bought peppers, potatoes, rice, sea kale, champignons, Pine nuts, dates, pickled bracken, corn on the cob, bananas and squid. Based on the modern hierarchical classification, how many different kingdoms do these objects belong to:
The fruit of a birch is called:
B) a nut; +
B) single-bone;
D) seed. 
a) with the help of trachea;
B) anaerobic way;
B) through the outer covers; +
D) does not occur at all, since it lives in soil where there is no oxygen.
Of the listed arthropods, antennules use for movement:
B) water donkey;
B) shrimp
D) cyclops. +
Which of the amphibians prefers the aquatic habitat:
B) toad, pond frog, lake frog; +
C) toad, pond frog, toad, newt;
D) garlic, newt.
The aorta in birds emerges from:
B) right atrium;
B) left ventricle +
D) right ventricle.
Frogs eat:
B) predominantly animal food;
C) larvae - mixed, adults - animal; +
D) larvae - animal, adults - mixed. 
a) quail;
B) capercaillie;
B) partridges; +
D) black grouse.
On the aerodynamic properties of a bird in flight do not affect feathers:
B) contour.
B) steering;
D) downy. +
This dental formula: i 3/3; c 1/1; pm 4/4; m 1/2 = 38, where i are incisors, c are canines, pm are premolars, m are molars, belongs to:
b) a boar;
c) chimpanzee;
d) badger . +
Striated muscle fibers are characteristic of muscle tissues that provide:
B) compression of the walls of the lymphatic vessels;
D) contraction of the bladder.
The human thoracic vertebra is composed of:
B) head, neck and processes;
C) bodies, arches and processes; +
D) body, arch and two spinous processes.
To the parts of the human small intestine not applicable:
B) skinny;
B) duodenal
D) iliac.
The period of eruption of permanent teeth in humans:
B) 2 - 3 years;
C) 6 - 7 years; +
D) 9 - 10 years. 
a) osteoblasts; +
B) osteocytes;
B) osteons;
D) osteoclasts.
The ureter connects:
B) kidney with the environment;
C) the bladder with the external environment;
D) kidney and bladder. +
Cells thyroid gland do not produce hormone:
B) thyrotropin; +
B) thyroxine;
D) triiodothyronine.
The taste zone most sensitive to bitter is located:
B) the root of the language; +
C) lateral edges of the tongue;
D) edges and tip of the tongue.
Features of the first signaling system:
B) the stimulus is the word;
C) stimuli are specific signals from the environment; +
D) is not characteristic of a person.
Fertilization in humans occurs in:
B) ovary;
C) the lower third of the oviduct;
D) the upper third of the oviduct. +
Sunbathing helps:
B) increased blood circulation; +
C) increased sensitivity of receptors;
D) the formation of vitamin E.
Cell center centrioles contain:
b) 27 microtubules grouped by 3; +
c) 20 microtubules forming 9 pairs along the periphery and 2 microtubules in the center;
D) 19 microtubules forming 9 pairs along the periphery and 1 microtubule in the center. 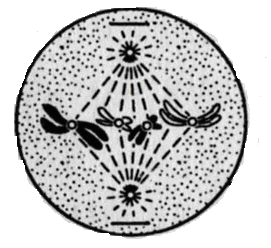
a) one nucleotide;
B) two nucleotides;
C) three nucleotides; +
D) four nucleotides.
In most food chains, energy intake depends mainly on:
B) the degree of efficiency of the cycle of substances of the ecosystem as a whole;
C) food activity of primary consumers;
D) heat losses during respiration at each trophic level.
When the temperature rises above 20-25ºС, the rate of photosynthesis decreases, because:
B) stomata close, which prevents the penetration of CO 2; +
C) the denaturation of enzymes that catalyze the reactions of photosynthesis begins;
D) the excitation of electrons in chlorophyll molecules decreases.
Factors limiting life in the hydrosphere:
B) lack of light and low pressure;
C) low temperature and high pressure;
D) high temperature and high pressure.
For the first time the skeleton of Archeopteryx was found:
B) in the middle of 1820. in France;
C) at the beginning of 1860 in England;
D) at the end of the 18th century in the USA.
The elementary unit of evolution is:
B) a separate individual of one species;
C) a set of individuals of several species united by kinship;
D) a population of individuals of the same species, united by kinship. +
The process of developing external similarity in unrelated forms of organisms that lead the same way of life in similar conditions is called:
b) phylogenesis;
c) symbiosis;
d) adaptation.
An example of mimicry is:
B) a change in body color in a chameleon;
C) the resting position of the praying mantis;
D) similarity in color and body shape of a caterpillar with a knot. +
The success of living on land for reptiles provided the following aromorphosis:
b) an increase in the number of sections of the spine;
c) the appearance of teeth;
d) the appearance of embryonic membranes. +
An increase in the number of migratory birds that do not fly south, but winter in large cities, should be considered the result of:
b) mechanisms of isolation and disruptive selection;
c) channeling selection and the appearance of isolation barriers;
d) stabilizing selection.
The Nobel Prize in Medicine and Physiology in 2012 was awarded to scientists Shinya Yamanaka and John Gurdon for their research:
b) by activation of innate immunity;
c) by pluripotency of stem cells; +
d) dendritic cells.
Part II.You are offered test tasks with one answer option out of four possible, but requiring a preliminary multiple choice. The maximum number of points that can be scored is 20 (2 points for each test task). The index of the answer that you consider the most complete and correct, indicate in the answer matrix.
The list of rare and endangered plants of the Red Book of the Republic of Bashkortostan (2007) includes:
II. May lily of the valley;
III. elecampane high; +
IV. tsmin sandy; +
V. lingonberry.
A) I, II, V;
b) I, III, IV; +
c) I, IV, V;
d) II, III, V.
A rhizome is different from a root:
II. the presence of reduced leaves; +
III. the presence of leaf scars; +
IV. the presence of a leaf cap;
V. the presence of an apical kidney. +
A) I, II, IV;
b) I, III, IV, V;
c) I, II, III, V; +
d) IV, V.
at the peony and shepherd's bag root cap:
II. formed by living cells; +
III. consists of cells containing starch grains; +
IV. promotes the advancement of the root in the soil; +
V. protects the apical meristem from damage. +
A) I, II, III;
b) II, III, IV, V; +
c) I, V;
d) I, IV.
Signs characteristic of a liver fluke are:
II. closed digestive system; +
III. always 22 body segments;
IV. hermaphroditism; +
V. open circulatory system.
A) I, II, IV; +
b) I, III;
c) I, II, IV, V;
d) II, IV, V.
Substances needed for blood clotting:
I. potassium.
II. calcium. +
III. heparin.
IV. prothrombin. +
V. fibrinogen. +
a) II, IV, V; +
b) I, IV, V;
c) I, II, IV;
d) II, III, IV, V.
During a quiet exhalation, the air "leaves" the lungs, because:
II. contraction of the intercostal muscles.
III. contraction of muscle fibers in the walls of the lungs.
IV. the diaphragm relaxes and takes on a domed shape. +
V. increases the volume of the chest.
a) I, IV; +
b) III, V;
c) I, III, IV;
d) I, II, IV.
Posterior pituitary hormones:
I. increase urination.
II. regulate the activity of the sex glands.
III. reduce urination. +
IV. increase smooth muscle contraction. +
V. regulate the activity of the adrenal cortex.
a) II, III, V;
b) III, IV; +
c) I, V;
d) I, II, IV.
The chloroplast and mitochondria are characterized by:
I. reproduction by division. +
II. localization in the cells of all living organisms.
III. localization in green prokaryotes.
IV. the presence of membranes. +
V. the presence of ribosomes. +
a) I, II, IV;
b) I, III, IV, V;
c) III, IV, V;
d) I, IV, V. +
In the process of photosynthesis, O 2 molecules are formed:
II. from a water molecule. +
III. in the stroma of the chloroplast and mitochondria.
IV. in the dark phase of photosynthesis.
V. in the light phase of photosynthesis. +
a) II, III, V;
b) I, IV;
c) II, V; +
d) II, III.
Of these animals, the composition of the steppe biocenosis includes:
I. hay pika. +
II. common viper.
III. little bustard +
IV. gray toad.
V. green toad. +
a) I, III, V; +
b) II, III, IV, V;
c) I, III, IV;
d) II, III, IV.
The bowl-shaped chromatophore has Chlamydomonas. +
Insect wings are located on the prothorax and mesothorax.
Characteristic inhabitants of swamps and coasts of reservoirs are the lark and the wagtail.
The order Insectivores includes the shrew, mole, and hedgehog. +.
The stomach of artiodactyls consists of sections: mesh, scar, book.
The method of anatomy that studies the microscopic structure of tissues and organs is called cytological.
In the human skull, the lacrimal bone is located behind the nasal bone.
The choanae open into the nasopharynx. +
The pancreatic duct opens into the stomach.
In the body of a man, in the absence of pathologies, female sex hormones are never formed.
The property of nervous tissue to transmit excitation is called irritability.
The nuclear chromatin is bound to proteins by histones. +
The human intestinal epithelial cell nucleus contains 44 autosomes and 2 sex chromosomes. +
Tunneling microscopy is used to study the relief of the cell surface. +
The collagen helix differs from the usual protein alpha helix in that it has branches.
The p-RNA molecule contains about 300 nucleotides.
During anaphase I of meiosis, the chromatids move toward the poles of the cell.
Translation is the translation of the nucleotide sequence of an i-RNA into the amino acid sequence of a polypeptide. +
In the light phase of photosynthesis, glucose is broken down into 2 molecules of pyruvic acid.
Features of microorganisms important for production are rapid reproduction and diploid genome.
1. [max. 5 points] Establish a correspondence between plant divisions (1, 2) and their characteristic features (A-Zh).
Characteristic signs:
A) have leaves, stems and roots;
B) leafy plants that do not have roots; +
C) these are avascular plants;
D) able to revive after complete drying;
E) spiral folding of young leaves;
E) the sexual generation (gametophyte) prevails over the asexual (sporophyte);
G) the sporophyte prevails over the gametophyte.
Department name:
1 - Bryophytes;
2 - Ferns.
[max. 5 points] Match the birds from the order Anseriformes (1-5) with their characteristic nesting sites (A-D).
| Birds | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
|
| nesting sites | G | AT | B | BUT | D | BUT |
[max. 5 points] Match the listed mammals (1-9) with their characteristic way of using the territory and food resources (A-B).
| Animal | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 |
| Way | BUT | AT | B | AT | BUT | B | AT | BUT | BUT |
4. [max. 5 points] Match the organic matter (A-E) and the name of the biological structures in which it can be found (1-6).
| biological structure | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 |
| organic matter | G | AT | BUT | B | E | D |
3. Mushroom poisoning
Mushroom poisoning occurs not only when inedible mushrooms are eaten, but also edible ones when they are improperly processed and preserved. Mushroom poisoning is quite common and sometimes ends in death, as the mushroom toxin is poisonous.
So, for example, morels and lines contain poisonous gelvellic acid, which can cause hemolysis (dissolution of red blood cells), damage the liver, heart, kidneys and spleen. The lines, in addition to gelvellic acid, also contain a whole group of very dangerous toxic substances, for example, gyrometrin, which, in addition to the ability to cause damage to the liver and other vital organs, also has a toxic effect on the nervous system and disrupts metabolic processes in the body, including cells brain.
Usually, the effect of the poison does not begin to appear immediately, but after 6-10 hours. The disease develops gradually. First, there is a feeling of fullness and squeezing in the stomach, acquiring over time the nature of pain and cramps, nausea occurs, turning into indomitable vomiting. Sometimes there is diarrhea, a rapidly growing feeling of weakness and weakness. Very often there is a sharp headache, confusion, delirium, convulsions, jaundice is often observed.
Particularly sensitive to the action of gelvellic acid and gyrometry are children, young people, pregnant women and the elderly.
It has been experimentally established that gelvellic acid is extracted from mushrooms by boiling. Unlike gelvellic acid, gyrometrin is soluble in hot water, heat treatment also does not affect it. But with prolonged drying, gyrometry and other substances of this group contained in the lines are still destroyed during prolonged drying.
In this way, correct handling mushrooms can eliminate the possibility of poisoning them.
Death cap- the most poisonous mushroom of all found on the territory of Russia.

The main role in the mechanism of poisoning with pale grebe is played by amanitotoxin. This substance is completely insoluble in water, retains its toxicity even after 20 minutes of boiling, and is not destroyed by enzymes. gastrointestinal tract.
The poison of the pale toadstool affects the liver, cells of the central nervous system, blood vessels, glandular tissue and the walls of the digestive tract. Along with this, the poison also causes a violation of many biochemical processes in the body.
Once in the body, the poison makes itself felt not immediately, but many hours after dinner or lunch. Meanwhile, the poison does its job, and when signs of poisoning appear, it is already difficult to save a person: the fungal toxin that has penetrated into the blood can be removed from the body only with the help of hemodialysis. Therefore, early hospitalization in a qualified medical facility can save a person who has been poisoned by a pale toadstool even when the fungal toxin is in the blood.
Fly agaric. The chemical composition of the fly agaric and the mechanism of its action on human organs are now well studied. The main poisonous beginning of fly agarics is the alkaloid muscarine, a strong poison, 3-5 mg of which kills a person (this amount of poison is contained in 3-4 fly agarics).

Fatalities are very rare and occur only when eating a large number these mushrooms. Recovery occurs relatively quickly: in 1-3 days. True, sometimes, due to some reasons, this period can be delayed up to 11 days.
False mushrooms, skillfully disguised as true ones, nevertheless fall into the baskets of inexperienced mushroom pickers, sometimes causing severe poisoning.
False mushrooms are not very toxic. When poisoned by these mushrooms, gastrointestinal disorders occur. These phenomena are associated with the action of the "milk" juice of false mushrooms, which has pronounced irritating properties and causes gastroenteritis (inflammation of the gastrointestinal tract), accompanied by nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, and diarrhea.
4. First aid for poisoning
First aid for accidental poisoning is of great importance to avoid serious health consequences. First aid to the victims should be provided immediately, since in case of acute poisoning, a violation of the basic vital functions of the body (respiration, heartbeat, blood circulation) can occur very quickly. Timely first aid contributes to a milder course of the disease caused by poisoning, and often prevents the possibility of death. You need to know that in case of poisoning, literally every minute is often precious. Therefore, everyone should be able to provide first aid to himself or the victim, without waiting for the arrival of medical workers.
Along with this, it should be remembered that first aid measures are only preliminary, urgent. At any degree of poisoning, with any toxic substance, a doctor should be immediately called to the victim.
In no case should you hide from doctors what substance was taken, as this makes it difficult to make a timely diagnosis, delaying the necessary assistance and reducing the chances of saving a life.
Methods of providing first aid depend both on the routes of entry of poisons into the body, and on their chemical composition.
When poison enters the body, it is necessary to give the victim to drink 6-10 glasses of warm water or a solution of baking soda; then, irritating the back wall of the pharynx and the root of the tongue (with a finger or a spoon), induce vomiting. The procedure should be repeated. After washing, the victim should take activated charcoal or slightly crushed carbolene tablets with water. Give milk to drink sweet tea, coffee. Give a laxative.
Before the arrival of the doctor, it is necessary to wrap the victim, warm with heating pads. With persistent vomiting, give pieces of ice to swallow.
If a toxic substance gets on the skin, it is necessary to remove this substance from the skin surface as soon as possible with a cotton or gauze swab or rag, trying not to smear it on the skin surface. After that, the skin should be washed well with warm water and soap or a weak solution of drinking (baking) soda.
If a poisonous substance gets into the eyes, immediately rinse them with a stream of water with the eyelids open. Washing should be thorough for 20-30 minutes, since even a small amount of a toxic substance that gets into the eyes can cause deep damage to the organ of vision. After washing the eyes, apply a dry bandage and immediately consult an eye doctor.
When poison enters through Airways it is necessary to remove the victim from a place with poisoned air to fresh air or take measures to quickly ventilate the room. Remove the victim from clothing that restricts breathing. The victim must be wrapped warmly, warmed with heating pads, allowed to rinse the throat and mouth with a solution of soda. If necessary, perform artificial respiration.
5. Treatment for poisoning
Treatment of victims of poisoning poisonous plants is carried out by removing the poison that has entered the body and reducing its toxicity with the help of various antidotes. It is very important to carry out the necessary measures in the order of self-help and mutual assistance before the arrival of a doctor or admission to a medical institution. Regardless of the type of plant poison that caused poisoning, it is urgent to induce vomiting by irritation of the pharynx or root of the tongue.
When excited, a cold compress is applied to the patient's head and they try to keep him in bed; when fainting, the patient in the supine position lowers his head down and raises his legs, give strong warm tea inside; when breathing and cardiac activity stop, artificial respiration and indirect heart massage are performed.
6. Prevention acute poisoning
Using medicinal plants at home without knowing them medicinal properties can be harmful to health and even cause death. Therefore, harvest healing herbs and it is necessary to prepare preparations for treatment from them very carefully and only with reliable knowledge of the matter, and not hearsay.
For the manufacture of medical preparations medicinal plants are widely used, such as lily of the valley, aloe, ergot, white hellebore, belladonna and many others. From them, under special conditions, medicinal substances are obtained that are of great benefit to patients in therapeutic doses. However, from these same plants at home (in decoctions, infusions, etc.) substances are obtained that can cause great harm, since, for example, set by eye treatment dose these substances is almost impossible. It is especially dangerous to use home remedies to treat children.
All preventive measures against poisoning with poisonous mushrooms come down to the following: it is necessary to remember well the distinguishing features of false mushrooms and pale grebe.
In general, the prevention of poisoning with plant poisons consists in the steady implementation of the following rules:
1. do not eat unfamiliar plants, mushrooms;
2. do not eat widely known cultivated plants (potatoes, cereals, buckwheat, peas, etc.) that have been improperly stored and overwintered in the field;
3. do not take home-made tinctures and herbal medicines without the doctor's consent;
4. do not spontaneously increase the dose prescribed by the doctor and the tincture prepared in the pharmacy;
5. do not allow children, especially younger ones, to pick mushrooms and berries on their own, without adult supervision;
6. do not trust your life and health to persons without special medical education, who offer “miraculous” for the treatment of diseases medicines made from plants.
From many conditions and, in particular, from the conditions of growth (terrain, weather). The lethal dose of pure muscarine is very small (about 0.01 g). Among spring mushrooms that can cause food poisoning, lines that are very similar to edible morel mushrooms should be mentioned. The main difference between the lines is the cellular structure on the section, while the morels on the section have ...
The drug is a colorless transparent oily liquid with a slight bad smell. Thiophos compounds are widely used for pollination and spraying of plants. In terms of toxicity, thiophos is not inferior to those strong poisons, how hydrocyanic acid and strychnine. According to foreign writers, the lethal dose of thiophos for humans is 6.8 mg/kg, i.e. about 0.5 g per adult. ...
Death can occur very quickly from primary cardiac arrest. Since the helpless state flutters very quickly during hanging, it is not possible to free oneself from the loop after it has been tightened. Thus, the main feature that distinguishes hanging from other types of mechanical asphyxia is a rapid loss of consciousness after being pulled ...
Despite the fact that everyone is aware of how dangerous it can be to eat them, hundreds, thousands of people are admitted to hospitals every year with a diagnosis of mushroom poisoning. The desire to profit from dishes from raw materials collected by oneself defeats the instinct of self-preservation and at times leads to sad consequences.
What mushrooms can be poisoned?
Many people love mushrooms. But sometimes this love is very dangerous consequences as severe poisoning. People mistakenly believe that only poisonous mushrooms can poison you. But in fact, edible fruits can also be dangerous. The fact is that in the legs and hats an environment favorable for the life and reproduction of bacteria is created. Heat treatment kills pathogenic microorganisms. But with improper preparation - if the pickles are stored for too long, or soaked in an insufficiently salted marinade, for example - poisoning with salted mushrooms is possible.
Is it possible to get poisoned? Yes, such cases also occur, although these fruits are considered the most harmless. The fact is that - even edible ones - they absorb toxins like a sponge. Therefore, they can become poisonous if stored improperly. This applies to raw, dried, and pickled mushrooms. Therefore, before cooking, it is better to study all the basic rules for processing and storage as carefully as possible.
How to distinguish poisonous mushrooms from edible ones?

The easiest way to protect yourself and prevent mushroom poisoning is to know which fruits are poisonous and which are not. There are many nuances and it will not be possible to remember everything at once. But after a few workouts, at a glance you will determine the "good" and "bad".
Here's how to distinguish poisonous mushrooms from edible ones and vice versa:
- Most edible mushrooms are tubular.
- Potentially dangerous fruits have an unpleasant greenish color. You should also be wary at the sight of a pinkish hat. These are mainly false mushrooms. Break it open to check. If the fungus is indeed false, the scrap will turn red. Do not trust too bright colors. In most cases, noticeable hats are an alarm.
- You can't rely on smell alone, but experienced mushroom pickers claim that poisonous prey either smells bad or doesn't smell at all.
- If you want to prevent poisoning with porcini mushrooms, put them all in a pot of water and throw an onion into it. If the latter turns blue, bad news: the crop will have to be thrown away.
- Inexperienced mushroom pickers bypass wormy fruits. But in fact, insects and animals almost always bury themselves only in edible mushrooms. There are exceptions, but they are rare.
Types of poisonous mushrooms
Knowing the main types of danger will also help prevent mushroom poisoning. There are a lot of them - it is believed that out of more than 3,000 species of edible mushrooms, only about 400 - but you don’t need to memorize everything. It is important to know only those that are mainly found in local latitudes. Among them are such instances:
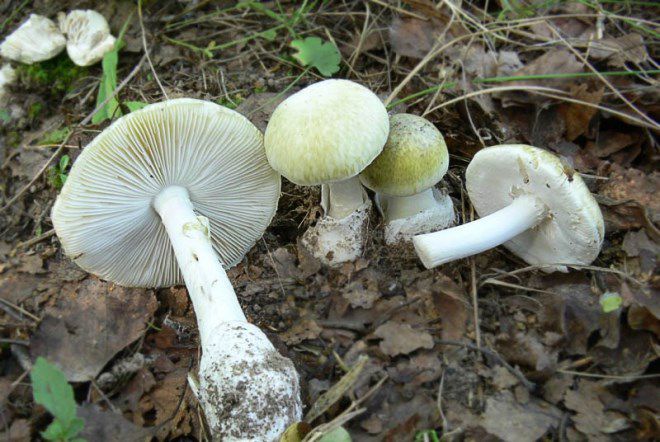

Symptoms of mushroom poisoning
This is very dangerous product, which can strike even after heat treatment or any other treatment. Therefore, if suddenly signs of mushroom poisoning appeared shortly after consuming this product, they urgently need to be paid attention to. Let the fears be better not confirmed than to have to face the unpleasant consequences of intoxication.
Mushroom poisoning, how long does it take for symptoms to appear?
As a rule, the first signs of mushroom poisoning begin to appear 1.5 - 2 hours after eating them. But sometimes the reaction comes in a day or even two. The time after which mushroom poisoning appears depends on various factors. The reaction rate is affected by the number of fruits eaten and their type, weight, age and health of the victim. Even the strongest the immune system unable to deal with the effects of toxins on its own. Therefore, sooner or later, signs of intoxication will appear.
The first signs of mushroom poisoning

It is almost impossible not to pay attention to them. Here is how mushroom poisoning manifests itself:
- nausea;
- severe vomiting;
- diarrhea up to 15 times per day;
- stomach ache;
- temperature rise to 38-39 degrees;
- upper and lower limbs become cold;
- inflammation of the stomach and intestines;
- weakening of the pulse;
- the appearance of delusions and hallucinations;
- marked mental disorder;
- anuria;
- increased sweating and salivation;
- breathing problems;
- drowsiness and weakness;
Poisoning with pickled mushrooms and botulism manifest similarly, but with slight nuances. Main symptoms:
- nausea with vomiting;
- diarrhea;
- severe headaches;
- blurred vision (begins to double in the eyes, everything floats);
- mucous oral cavity dries up;
- convulsions appear;
- breathing becomes difficult.
What to do in case of mushroom poisoning?
Self-medication for intoxication is strictly prohibited. Therefore, when poisoning with poisonous mushrooms occurs, the first and most important thing to do is to call specialists or try to independently deliver the victim to the emergency room of the nearest medical center. If it is possible to keep samples of the product, please do so. So experts will be able to find out which poison caused the poisoning, and more likely to select the appropriate effective treatment.
First aid for mushroom poisoning
The main thing to remember is that the victim cannot be harmed. No need to urgently dig into the Internet in search of practical advice. The main emergency aid for mushroom poisoning is gastric lavage. This is necessary to remove the remaining toxins from the body. First aid for poisoning with poisonous mushrooms involves drinking plenty of water. The patient can be given tea, water or a weak solution of potassium permanganate, and then induce vomiting by pressing on the root of the tongue. The procedure should be continued until the remains of food stop coming out of the stomach.
Mushroom poisoning - what to do at home?
In addition to drinking plenty of water, laxatives and tablets can be given to victims. activated carbon. If mushroom poisoning occurs, home treatment involves the maximum effective cleansing stomach and intestines. Because coal is the best help. It is an effective sorbent. Take it should be 1 piece per kilogram of body weight. But if the patient has symptoms - low blood pressure, loss of consciousness, convulsions - the above methods can be harmful.
Mushroom poisoning - hospital treatment
The first thing they do in the hospital is to insert a probe and use it. Often, with a problem of mushroom poisoning, treatment involves taking a saline laxative, intravenous administration of drugs and accelerated diuresis. On the first day, hemosorption is carried out and toxins are removed from the blood. In the presence of hallucinations, the patient is given the antidote Atropine.
Mushroom poisoning - consequences
The most dangerous toadstool poisoning. It ends in death in 50-90% of cases. If the patient eats up to 3 fruits, death occurs in 100% of cases. When using other species, the consequences of mushroom poisoning may be less critical. In the case when treatment begins on time, the person is fully restored. If assistance was not provided, then within 5-8 days death occurs with a 50 percent probability.
Prevention of mushroom poisoning
The easiest way to buy mushrooms in proven places. But if the passion to collect fruits cannot be overcome, here are some tips on how not to get poisoned by mushrooms:
- Do not pick unfamiliar fruits.
- Try to avoid old mushrooms.
- When cooking, do not forget to carefully process and boil hats with legs. Discard the first few broths.
- Mushrooms should be cleaned and cooked immediately after harvest.
- No need to collect anything near roads and industrial areas.
- Do not collect mushrooms in plastic bags. It is best to use baskets.
- If mushroom canned food has a swollen lid, it is safest to throw it away.