Pale grebe venom at autopsy. strong poisons
The name of the mushroom comes from the Latin "Amanita phalloides". Intoxication from this type of fungus leads to a high mortality rate worldwide.
Even more experienced mushroom pickers they can confuse this poisonous mushroom with champignons or russula, which becomes the worst mistake of their life. What to do in case of intoxication we learn from this article.
What is poisoning and its causes?
This is a negative incident, which is the result of a fungus entering the human digestive tract, which causes harm to all internal organs.
The causes of poisoning are considered to be the eating of the fruiting body of a poisonous mushroom or some part of it. This may happen by accident or on purpose.
In case of intentional poisoning the fungus enters the body as a result of illegal guilty or careless actions of unauthorized persons or as a result of one's own decision.
High degree of poisoning due to the fact that this mushroom is very easy to confuse with other edible mushrooms, such as greenfinch, champignon, and russula.
Symptoms of poisoning
Even in the smallest amount, pale grebe can be fatal.
By palatability mushroom has a very pleasant taste, which makes it indistinguishable from edible mushrooms during food consumption. The first signs of poisoning can occur after 8 hours. The latent period can last up to 48 hours, which only exacerbates the poisoning process.
To the main symptoms of poisoning can be attributed:
- severe diarrhea (in some cases with impurities of blood in the feces);
- the occurrence of a feeling of thirst;
- intestinal colic;
- pain in the abdomen;
- cyanosis of the skin (acquiring a pale appearance of the skin);
- a significant decrease in body temperature;
- cramps in the limbs.
Depending on the clinical picture intoxication can be divided into:
- light;
- average;
- heavy.
When mild intoxication moderate gastroenteritis appears, and liver damage occurs (mild hepatopathy).
At medium degree gastroenteritis poisoning is already pronounced, liver damage is observed in the form of toxic hepatopathy, kidney damage is noted - nephropathy in a moderate or mild degree.
Severe degree intoxication has clearly expressed severe forms damage to the liver and kidneys, up to their insufficiency, as well as severe gastroenteritis.

Stages of intoxication with pale toadstool
Modern literature conditionally divides poisoning into stages:
- latent, or as I call it the incubation period. It can last up to 8 hours to several days. At this stage there are no signs of food poisoning;
- stage of acute gastroenteritis, which is characterized by inflammation of the mucosa in the small intestine, as well as severe pain in the abdomen, vomiting and diarrhea. This stage can last up to two days, and in some cases longer;
- "calm stage". During this period of time, visible improvements in health are observed, which are temporary. In the real state of the victim, there are no shifts towards improvement;
- stage of damage to parenchymal organs. At this time, acute hepatic, as well as kidney failure. A large proportion of the likelihood of such a negative consequence as the death of the victim;
- in the event that the death does not occur, we can talk about the period of recovery.
Toxins that cause poisoning
Modern science subdivides the toxic substances or toxins that are in the fruiting body of the pale grebe and can cause irreparable harm person, into several groups:
- amanin;
- amanitins (they include amatoxins, as well as amanitotoxins);
- phalloidins or phallotoxins.
It should be noted that action of amanitins much faster than phalloidins, but nevertheless they are considered not as poisonous.
All these substances are capable affect mainly liver cells. They accumulate in hepatocytes and, subsequently, lead to their destruction. "Phalloidin syndrome" may develop.
In this case, necrosis of the liver occurs, the kidneys, the entire gastrointestinal tract, and also blood cells can be affected.
The strongest and most dangerous intoxication can occur in young children, as well as in older people and those who have serious illnesses internal organs especially kidney and liver.

Clinical picture of poisoning
- As is already clear from this article with pale toadstool, the latent period is characteristic, that is, the period that passes without any manifestation of signs.
- After its completion,sudden onset of uncontrollable vomitingand severe nausea. Diarrhea occurs up to twenty times a day and stools look like rice water with the presence of blood and mucus in them. Signs of dehydration become very pronounced. The patient's condition is accompanied by a pronounced dryness of all skin, as well as mucous membranes.
- The next stage is very dangerous - this is the stage of the so-called calm and well-being. It comes on about the third day and can last up to four days. Outwardly, the person has no complaints, however toxic substances continue their negative impact on the liver. During this stage, kidney and liver failure develop.
- Fatal outcome can occur on the twelfth day, and in the absence of treatment even on the first day. Therefore, the sooner the victim seeks full medical treatment, the better for him and his health.
Help with pale grebe poisoning
- In the event of the onset of the first signs of a deterioration in well-being after eating mushrooms it is necessary to rinse the stomach very quickly and thoroughly. This will make it possible not to get into the blood of toxic and toxic substances, which will reduce the risk of onset negative consequences.
- For gastric lavage, use warm water, and in the absence of such, you can use any water. The victim should be allowed to drink about one sheet of water and provoke a gag reflex by irritating the base of the tongue with the fingers.
- This procedure must be repeated several times until complete cleansing. As a rule, washing is repeated about five times.
- When admitted to the hospital, the victim is cleansed of the stomach with a probe. This type is considered more efficient and effective.
- A laxative in the form of magnesium sulfate inside (30 ml). Activated charcoal, polysorb, smecta, enterosgel and other sorbents help fight against intoxication of the body.
- As an antidote and lipoic acid may be prescribed. Acetylcysteine is able to have a direct, indirect and non-specific antitoxic effect. He is prescribed one hundred milliliters of a one percent solution inside.
- official and also ethnoscience acknowledged that any medicinal preparations made on the basis of milk thistle(karsil or silibor) effectively fight against toxic poisoning liver, which is caused by intoxication after taking pale grebe.
- Atropine is administered intravenously to the victim with severe bradycardia.
- In case of intoxication, it is necessary to constantly monitor the level of water balance and fight dehydration.

At the slightest suspicion of poisoning poisonous mushrooms- with a pale toadstool, it is urgent to provide the victim with urgent medical care, as well as call competent specialists.
Particular attention should be paid specifically to calling a doctor and receiving assistance in a hospital hospital or other competent authority, so that there is a real opportunity to avoid the onset of negative consequences in the form of a long-term health disorder, as well as death.
Take care of yourself and your loved ones!
Superiority, among severe food poisoning, is occupied by a pale grebe. The chance of death is ninety percent. Pale grebe is the most terrible and poisonous representative of mushrooms. That is why it is necessary to know why it is dangerous, how to recognize the signs / symptoms, as well as first aid rules.
The difference between pale grebe
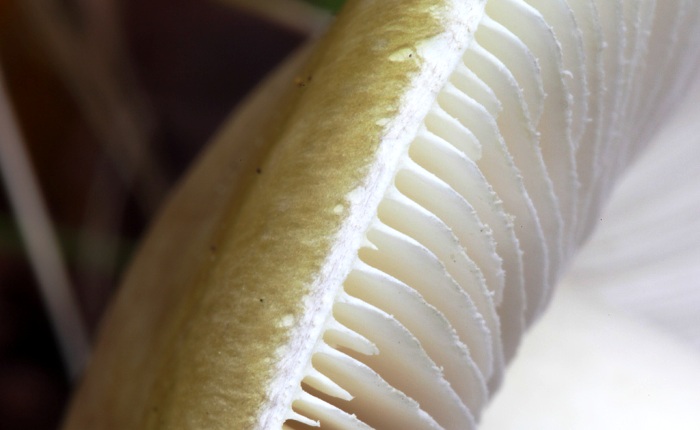
The peculiarity of the structure of such a fungus is that it has a specific ring located on the stem. In addition, a special bag (Volva) is located at the bottom of the leg, its width is three to five centimeters. Toadstool differs from ordinary champignon in that its caps are always white. Taste and smell are practically not expressed, and the pulp is always the same color.

Pale grebe: the main differences with similar mushrooms:
- champignon - after a certain amount of time, the cap becomes brown, and there is also no Volvo;
- float - small size, no ring;
- greenfinches, russula - they do not have a Volvo, a ring.
Very important! Never make the following mistake - you can not cut the mushrooms to the very hat, so there is a risk that you will not notice the presence of those features that the toadstool has.
Pale toadstool poisoning occurs at certain times of the year, namely from July to October. A boom in poisonings is observed, recorded in the last month of summer - August.
Symptoms of poisoning and consequences
Symptoms of pale toadstool poisoning depend on the amount of poison that has entered the human body, as well as the severity of the disease. Symptoms appear in four periods.
First period
Latent or without frightening signs. Duration seven to forty hours. This allows specialists to establish an accurate diagnosis, and is also the cause of severe consequences. A long asymptomatic time poses a direct threat to life, since the main part of the poison enters the bloodstream, then begins an active destructive activity.
Second period

Duration is about two days, sometimes six. Very frequent diarrhea (yellow, green color), after a certain amount of time acquires a mucous, watery structure with droplets of blood. This is the most obvious symptom. Then there is an excruciating thirst, profuse vomiting that accompanies each fluid intake.
From the gastrointestinal tract there are spasmodic painful colic, increased gas formation. As a result of a large loss of fluid in the body - falls arterial pressure pulse quickens, dizziness appears, headache, lack of urine. Diarrhea and vomiting - are the cause of excretion from the body - which leads to the development of frequent, painful convulsions.
Third period
Characterized by a deceptive recovery. Duration no more than twenty-four hours. There is an improvement in well-being, at the same time there is a violation of the liver. If the poisoning with a pale toadstool is strong, then after ten to thirteen hours, a collapse occurs, and then death. Doctors say that the third period of poisoning is the most dangerous and critical.
The fourth period

It is marked by the defeat of most internal organs. Characteristic symptoms: jaundice, severe diarrhea, colic, hepatitis, nephropathy develops. Then comes hepatic/renal and heart failure, resulting in a fatal outcome of the disease.
When poisoning with this fungus occurs, the main and frequent period the onset of death - the first ten days after its use in food.
A huge role is played by the amount of poison taken, as well as the general condition of the body (especially blood vessels, heart), as well as the presence of concomitant, chronic diseases. Recovery after poisoning is complete - there is a resumption of the functioning of all internal organs.
First aid
Quite often it happens that the first aid provided to the victim does not give relief, due to the long-term influence of mushroom poison. If you suspect poisoning, call immediately ambulance or go to the clinic. If you go to a medical institution and receive treatment within the first thirty-six hours, after using the mushroom in food, the prognosis will be favorable, comforting.
The main detoxification activities that must be done before the ambulance arrives:
- wash the stomach with a manganese solution (two to three liters), induce vomiting;
- give the victim Activated carbon;
- plentiful drink.
Treatment in the hospital is difficult, as the poison has spread through the blood. Actions performed in the hospital in case of toadstool poisoning:
- gastric lavage;
- the fight against dehydration of the body is carried out with the help of the following medications: trisol, saline, acesol, droppers with glucose;
- make forced diuresis;
- means for the heart to stimulate its activity;
- vitamin B, riboxin and others.
The result of the treatment of mushroom poisoning depends on the amount of poison that has entered the human body, as well as the state of health of the victim.
Preventive actions

To prevent poisoning dangerous mushroom, like a pale toadstool, you must remember that you can not pick mushrooms that are unfamiliar / suspicious to you. It is important to remember the main rules of the mushroom picker, which will help save your life:
- avoid unfavorable places for collection - industrial areas, landfills, roads, roadsides, etc.;
- pluck well-known mushrooms;
- pay attention to its quality - smell, color, elasticity.
In case of poisoning with a fungus such as pale toadstool, urgently contact the ambulance.
Amantotoxin
Description
It is an alkaloid found in the pale grebe. AT pure form you do not select it - and it is not necessary.
Basically, inside. Poisoning food and drinks. In time " mushroom season» you can throw pieces of toadstool in mushroom dish to your enemy. Or present him with a jar of pickled mushrooms (of course, not on his own and not on his own behalf). Poisoning will look like an accident. You can isolate the amantotoxin extract from the mushroom and add it in drops to food at any time of the year. In this case, the poison cannot be identified at all. You can apply the poison by explication.
Toxic properties and doses
This is one of the most toxic substances of plant origin. In terms of toxicity, it is inferior, perhaps, to the poison curare. There is a known case of poisoning when the victim did not wash his hands after holding pale grebe and decided, then, to eat a pie ... Amantotoxin very quickly destroys the liver and kidneys. mld = 2 g fresh mushroom or 20 drops of juice.
It is noteworthy that the symptoms of poisoning do not appear immediately, but after 4-12 hours from the moment the poison enters the body.
* Attention! During this period, it is no longer possible to save the victim even with the most modern means of medicine.
So, the first symptoms are abdominal pain, indomitable vomiting and severe diarrhea. Urine becomes bloody. Feeling tired, constantly thirsty, cramps in the calf muscles. On the 3-4th day there is a period of "false well-being". The victim becomes better, the symptoms of poisoning subside. But it is at this moment that the increased destruction of the liver and kidneys begins. Death occurs in 4-6 days, despite the best efforts of doctors. There is no specific antidote. Amantotoxin does not decompose when heat treatment and drying.
How to do it
First you need to stock up on toadstools. There are several varieties of them, but you are interested in the "pale toadstool", as the most toxic fungus.
Belongs to the genus fly agaric, the fly agaric family, grows in coniferous and mixed forests, from July to October singly and in groups. The cap is up to 12 cm in diameter, at first bell-shaped, then flat-convex, prostrate, sometimes not fully opening, with a tubercle in the middle, pure white, in mature mushrooms it is slightly yellowish in the middle, usually without scales (remains of a common cover). The flesh is white, not bitter (do not * taste) with bad smell, especially in recumbent mushrooms. The plates are free, pure white. Leg up to 8 cm long, up to 2 cm in diameter, even, sometimes curved, thickened towards the base, white with scales, with a white sagging ring under the cap itself (the ring sometimes grows on one of the sides to the cap). At the base of the leg, there are loose white remnants of a common coverlet - a bag-shaped volva, which hides the thickened lower part of the leg. Spore powder is white. A young toadstool mushroom in a common coverlet looks like egg. It must be borne in mind that if you pick this mushroom by holding the leg, then the Volvo may remain in the ground. In short, look at the picture.
It is not necessary to collect a full bucket. 2-3 pieces will be enough for you.
Gather young mushrooms - poison from them will have less disgusting smell and less likely that the victim will notice it.
Now let's recycle raw materials
The easiest way is to dry. Mushrooms just need to be cut in small pieces and put in a draft (can be under a conventional or thermal fan).
* Attention! All operations with toadstool should be carried out only with gloves and a respirator (gauze bandage). Dishes and a knife used for processing raw materials can no longer be used for food purposes!
After about 6-24 hours, the mushrooms will dry out. Grind them in a wooden mortar to powder.
* Attention! The operation is carried out only in the open air with a gauze bandage!
1-2 g of this powder will help you solve any problem related to the "human factor".
This magical powder can be stored for up to a year in a dry cool place without losing its wonderful properties.
Let's go further. Can you do it differently
crumble fresh mushroom in a jar and fill with 70% alcohol. For 1 medium mushroom you need about 150 ml of alcohol. Close tightly. Leave to infuse in a dark place for 2 weeks. Shake occasionally. Drain the alcohol and wring out the rest of it well with a spoon of mushroom pieces. Throw away the mushroom, and pour the alcohol into a small bottle. Do not close the cork, but put the bottle in a warm place. The alcohol will start to evaporate. Don't rush the process! When about 50 ml remains, screw tightly with a cork. The poison is ready. mld = 10 ml.
Hypertonic extraction
Cut the toadstools and put them in a jar, about halfway. When folding mushrooms, sprinkle them with sugar (as for jam) or salt. Close tightly and leave to stand overnight. The sugar will draw the juice out of the toadstool and a thick liquid will form at the bottom of the jar. Carefully drain it, squeezing the mushrooms with a spoon, into a vial and close tightly.
You've got a kind of mushroom syrup. It can be stored in the refrigerator for up to a year without loss of properties. Depending on what you sprinkled mushrooms with (sugar or salt), your syrup will have the appropriate taste (don't try it). Accordingly, it can be added to different dishes so that the victim does not notice the change in taste. So to speak, sweet to sweet, dust to the ground ...
The strongest toadstool poison
Finely chop and squeeze out pure juice. Add alcohol to the juice at the rate of 0.5 ml of alcohol per 10 ml of juice. Store tightly sealed in the refrigerator. mld = 1 ml.
Now even tougher
Squeeze out the juice, as in the previous one, pour it into a vial with a fairly wide neck, and place the (open) vial in a sand bath at +60°..+75 °C. Let it slowly evaporate to 1/5 of the original volume. If it thickens, don't worry. Try not to overheat too much. In the resulting extract, add 70% medical alcohol. Approximately 0.5 ml of alcohol per 10 ml of extract. mld = 0.5 ml.
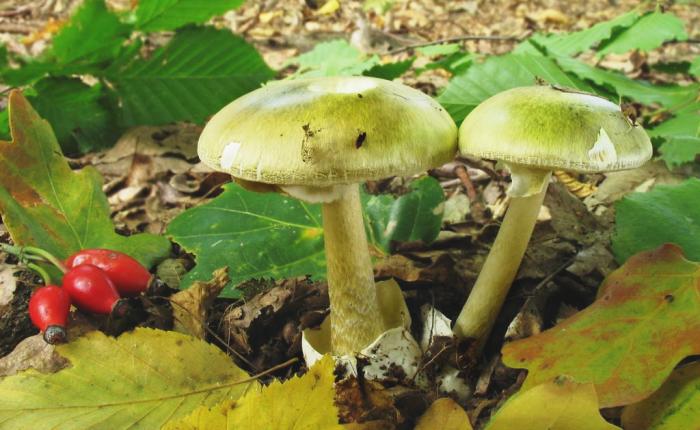
The pale grebe (Amanita phalloides) is one of the most poisonous mushroom species. Mortality in case of poisoning with it is 99%. The pale grebe has an olive, greenish or grayish hat 5-15 cm in diameter, with a smooth edge and a fibrous surface. Leg 10-15 cm long, whitish in color with a thickening at the base. Most often, the pale grebe is confused with champignons, green russula and greenish russula, with floats.
The pale grebe is widespread in the temperate zone of Europe, Asia and North America. The fungus often grows near deciduous trees- oak, beech, hazel. The season starts at the end of summer and continues throughout autumn.
Pathogenesis
Pale grebe belongs to the group of hepatonephrotoxic fungi. It contains two types of toxins - more poisonous, but slower acting amanitins and less poisonous, but fast acting phalloidins. The latter are not destroyed even after twenty minutes of cooking at 100°C.
The point of application of the toxins of the pale toadstool is the liver. In hepatocytes, under the action of phalloidins and amanitins, the destruction of the endoplasmic reticulum and the cell nucleus occurs. Thus, the use of pale grebe leads to fatty degeneration of the liver.
Clinic
The incubation period for poisoning with pale toadstool lasts from 6 to 30 hours. Next, the period of appearance of signs of damage begins. gastrointestinal tract. A poisoned person suddenly develops abdominal pain, vomiting, and profuse diarrhea. It is accompanied by thirst and weakness. Increasing intensity of vomiting and diarrhea can lead to severe dehydration. This period lasts from 1 to 6 days.
This is followed more often by a period of so-called imaginary well-being. At the same time, the signs of gastroenteritis gradually disappear, which leads the doctor to an erroneous opinion about the patient's well-being. Meanwhile, biochemical parameters of blood testify to damage to hepatocytes (increase in the level of transaminases, bilirubin, decrease in the level of prothrombin). The period of imaginary well-being lasts no more than a day.
After 10-12 hours, clinical signs of toxic hepatitis appear - icterus of the sclera, mucous membranes and skin, heaviness and pain in the right hypochondrium, liver enlargement. This is the period of damage to parenchymal organs, when liver and kidney failure develops.
Diagnostics
Unfortunately, in most hospitals in the CIS countries, when making a diagnosis of pale toadstool poisoning, the doctor is forced to be guided only by an anemnesis, clinic and biochemical parameters of the blood. In a number of hospitals in highly developed countries, it is possible to determine the presence of ammanitins in the urine within two to three days from the moment of eating mushrooms. This greatly simplifies the diagnosis and tactical measures.
Emergency care for poisoning with pale toadstool
The first urgent measure for poisoning with pale toadstool is the removal of unabsorbed toxins from the gastrointestinal tract. It is necessary to induce vomiting, if not, and to wash the stomach. After washing, give the patient activated charcoal at the rate of 1g/kg.
The above actions can be carried out before the ambulance team, before the patient enters the hospital.
In the department acute poisoning or in the intensive care unit, the water-electrolyte balance is corrected with the help of infusion media - acesol, trisol, Ringer's solution, saline.
There is no consensus on antidote therapy for poisoning with pale grebe. It is known that benzylpenicillin can be used as an antidote, which is used up to three days from the moment of eating mushrooms at a dose of 500 thousand-1 million/kg of body weight per day in 6 doses. Silibinin is prescribed at a dose of 30 mg/kg of body weight per day for 10-12 days after the onset of the disease. Recently, it has been reported good results the use of lipoic acid for poisoning with pale toadstool ( daily dose 300 mg).
AT complex therapy Toadstool poisoning can be treated with forced diuresis as a means of detoxification. Prevention of DIC is carried out by the use of proteolytic enzymes - contrykal, gordox.
The protection of the liver in patients with poisoning of the pale toadstool is achieved by the introduction of B vitamins, nicotinamide, and riboxin into therapy.